
Cyber threats to watch for in January 2023
According to our analysis of recent data, a significant increase in the number of indicators of compromise (IoCs) has been observed in December 2022 for some of the threat-related entities in our database. This trend appears to be continuing into the beginning of 2023, with specific cyber threat entities identified as the main contributors. These threats are believed to still be active and pose a ongoing risk.
We see an abnormal growth in the number of indicators attributed to those particular entities below:
- Raccoon (Stealer)
- Xmrig (miner, not malware)
- Gamaredon (threat actor)
- Icedid (banking trojan, also known as BokBot)
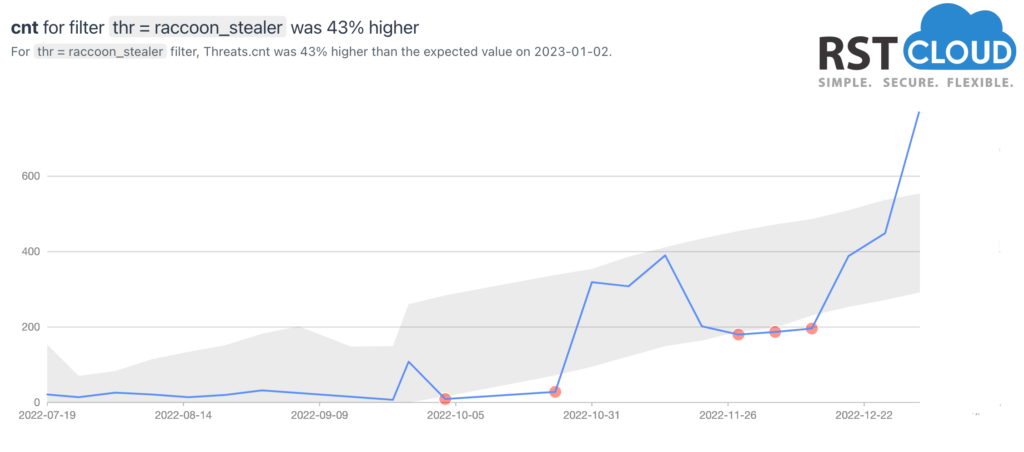
The Racoon stealer is a type of malware that is used to steal sensitive information from infected computers. It is typically sold as a “Malware as a Service” (Maas) which means that cybercriminals can purchase and use the malware without having to develop it themselves. In December 2022, we have seen a significant increase in the number of indicators related to the Racoon stealer. This trend began in October and continued to grow throughout the end of the year. This suggests that the popularity of the Racoon stealer is increasing among cybercriminals and that it is becoming a more widely used tool for information theft. It’s also possible that the malware creators have been working to improve the malware and making it more stealthy.
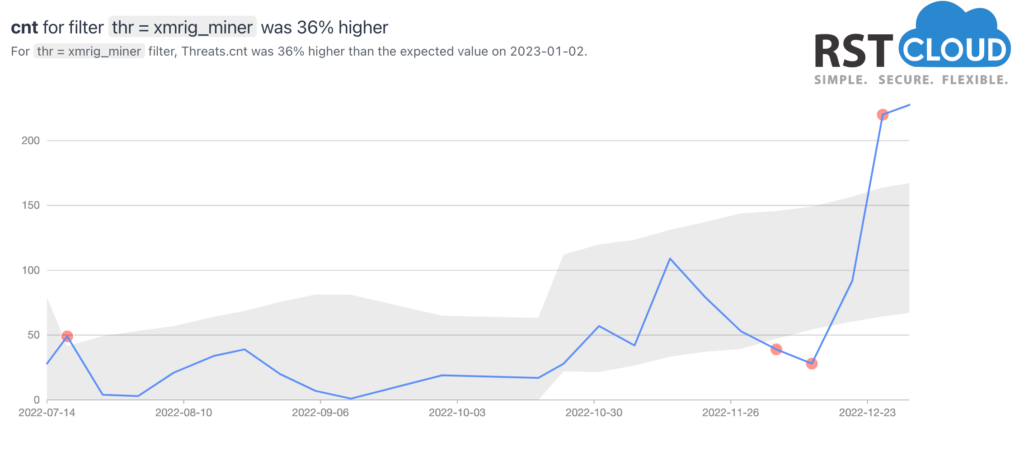
XMRig is a widely-used open-source software for mining cryptocurrency such as Monero or Bitcoin. While it is not inherently malicious, it is often utilized by threat actors for illicit mining activities. Cryptomining malware, known as “cryptojacking,” remains prevalent despite the recent decrease in the value of Bitcoin compared to its peak in 2022.
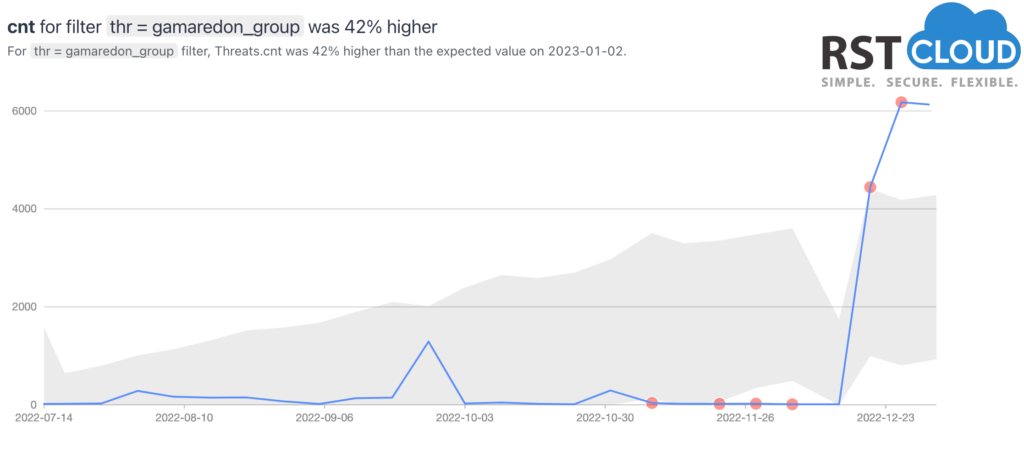
The Gamaredon Group is a cyber threat actor that has been associated with Russia. They are known for their use of spearphishing and malware in targeted attacks against government and military organizations, as well as against businesses in various industries. The group has been active since at least 2013, and it is considered a significant threat due to its advanced capabilities and persistence.
In December 2022, it appears that the Gamaredon Group was particularly active, with many indicators pointing to a rise in their activity during this time. The group is known for using a variety of malware and tools in their attacks, including custom malware, Remote Access Trojans (RATs), and backdoors. They have also been observed using living-off-the-land tactics, where they leverage legitimate tools and utilities for malicious purposes.
Gamaredon group also been seen leveraging social engineering tactics as well as taking advantage of known vulnerabilities in software, to spread its malware payloads.
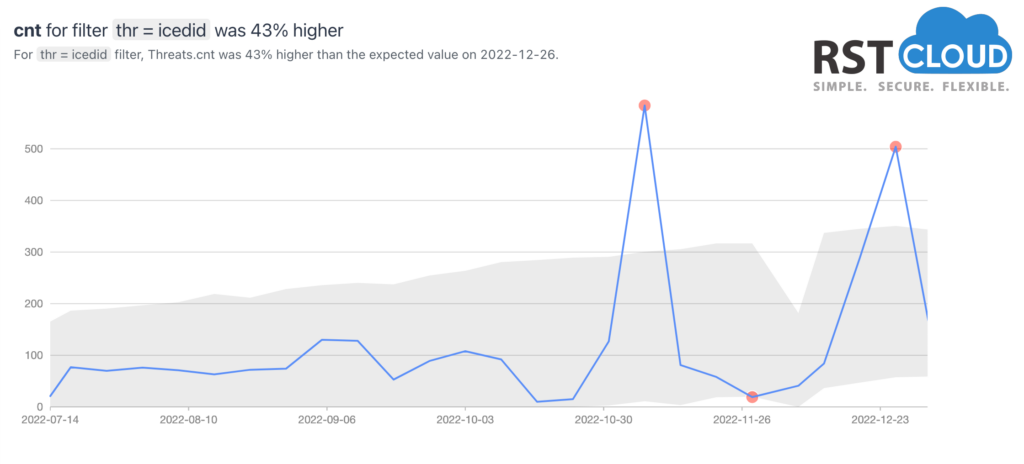
IcedID is a banking trojan-type malware which allows attackers to utilize it to steal banking credentials of the victims.
The full details about all of the IoC related to these entities are available in our RST Threat Feed. These entities pose ongoing risks and it is important for organizations and individuals to remain vigilant in protecting against them in the beginning of 2023. Keeping software and systems up to date, practicing safe browsing habits and using robust security solutions integrated with threat intelligence feeds can help mitigate the risks posed by these threats.